这里演示构建一个回归模型预测房价的方法。
= xfun:: magic_path ("ch6_house.csv" )<- readr:: read_csv (file)
Rows: 21613 Columns: 10
── Column specification ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Delimiter: ","
dbl (10): price, bedrooms, bathrooms, sqft_living, sqft_lot, floors, conditi...
ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data.
ℹ Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.
# A tibble: 21,613 × 10
price bedrooms bathrooms sqft_living sqft_lot floors condition grade
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 221900 3 1 1180 5650 1 3 7
2 538000 3 2.25 2570 7242 2 3 7
3 180000 2 1 770 10000 1 3 6
4 604000 4 3 1960 5000 1 5 7
5 510000 3 2 1680 8080 1 3 8
6 1230000 4 4.5 5420 101930 1 3 11
7 257500 3 2.25 1715 6819 2 3 7
8 291850 3 1.5 1060 9711 1 3 7
9 229500 3 1 1780 7470 1 3 7
10 323000 3 2.5 1890 6560 2 3 7
# ℹ 21,603 more rows
# ℹ 2 more variables: sqft_above <dbl>, yr_built <dbl>
house_raw 是著名的 “King County House Prices” 数据集。
对数据集的说明
这个数据集包含了美国华盛顿州金县(其中包括西雅图)的房屋销售价格以及相关房屋特性。
以下是一些列的描述:
price: 房屋销售价格,这通常是我们要预测的目标变量。bedrooms: 卧室数量。bathrooms: 浴室数量。sqft_living: 居住面积(平方英尺)。sqft_lot: 地块大小(平方英尺)。floors: 楼层数。condition: 房屋状况,一般是按照某种等级划分的。grade: 根据 King County 分级系统评出的房屋等级。
这个数据集经常被用来进行回归分析或机器学习任务,例如预测房价。
传统方法
下面是由 “Jia-Qi He” 在 “2022/9/11” 创作的传统方法。
Load Library
## 加载程序包,使用里面的管道函数 library (dplyr)
The following objects are masked from 'package:stats':
filter, lag
The following objects are masked from 'package:base':
intersect, setdiff, setequal, union
## 设置随机数种子 set.seed (202209 )
Data Processing
读入数据,生成R数据框。将 price、sqft_living、sqft_lot、sqft_above 这四个变量取对数;并计算到 2015 年时房屋的年龄。
<- house_raw %>% mutate (log_price = log (price)) %>% mutate (log_sqft_living = log (sqft_living)) %>% mutate (log_sqft_lot = log (sqft_lot)) %>% mutate (log_sqft_above = log (sqft_above)) %>% mutate (age = 2015 - yr_built)
使用 sample() 函数将数据集随机划分为学习数据集和测试数据集。先抽取学习数据集的观测序号,学习数据集是抽取的观测序号对应的观测。测试数据集是未被抽取到学习数据集的观测。
<- sample (1 : nrow (house), round (0.7 * nrow (house)))<- house[id_learning,]<- house[- id_learning,]
Fitting
对学习数据集拟合线性模型。因变量是 log_price,log_sqft_living 等变量均为自变量。
<- lm (log_price ~ log_sqft_living + log_sqft_lot + log_sqft_above + age + bedrooms + bathrooms + floors + condition + grade, data = house_learning)
查看建模结果。
Call:
lm(formula = log_price ~ log_sqft_living + log_sqft_lot + log_sqft_above +
age + bedrooms + bathrooms + floors + condition + grade,
data = house_learning)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-1.29041 -0.21109 0.01026 0.20526 1.67461
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 7.7428942 0.0735920 105.214 < 2e-16 ***
log_sqft_living 0.5174014 0.0161666 32.004 < 2e-16 ***
log_sqft_lot -0.0336378 0.0035713 -9.419 < 2e-16 ***
log_sqft_above -0.0871745 0.0152195 -5.728 1.04e-08 ***
age 0.0060742 0.0001142 53.181 < 2e-16 ***
bedrooms -0.0438852 0.0035787 -12.263 < 2e-16 ***
bathrooms 0.0773968 0.0059612 12.983 < 2e-16 ***
floors 0.0680483 0.0072774 9.351 < 2e-16 ***
condition 0.0343253 0.0043309 7.926 2.43e-15 ***
grade 0.2409012 0.0036670 65.694 < 2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Residual standard error: 0.3165 on 15119 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.638, Adjusted R-squared: 0.6377
F-statistic: 2960 on 9 and 15119 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16
模型中各个自变量的系数均显著不为 0;模型的 R 方为 0.6406。
提取模型的系数估计值
(Intercept) log_sqft_living log_sqft_lot log_sqft_above age
7.742894171 0.517401364 -0.033637793 -0.087174490 0.006074193
bedrooms bathrooms floors condition grade
-0.043885175 0.077396849 0.068048324 0.034325337 0.240901189
提取模型的因变量拟合值。
<- fitted (fit.lm)str (yhat)
Named num [1:15129] 13.1 13.2 13.4 13 13.4 ...
- attr(*, "names")= chr [1:15129] "1" "2" "3" "4" ...
提取模型的残差。
<- residuals (fit.lm)str (resid)
Named num [1:15129] -0.0141 -0.308 0.1671 -0.2173 0.443 ...
- attr(*, "names")= chr [1:15129] "1" "2" "3" "4" ...
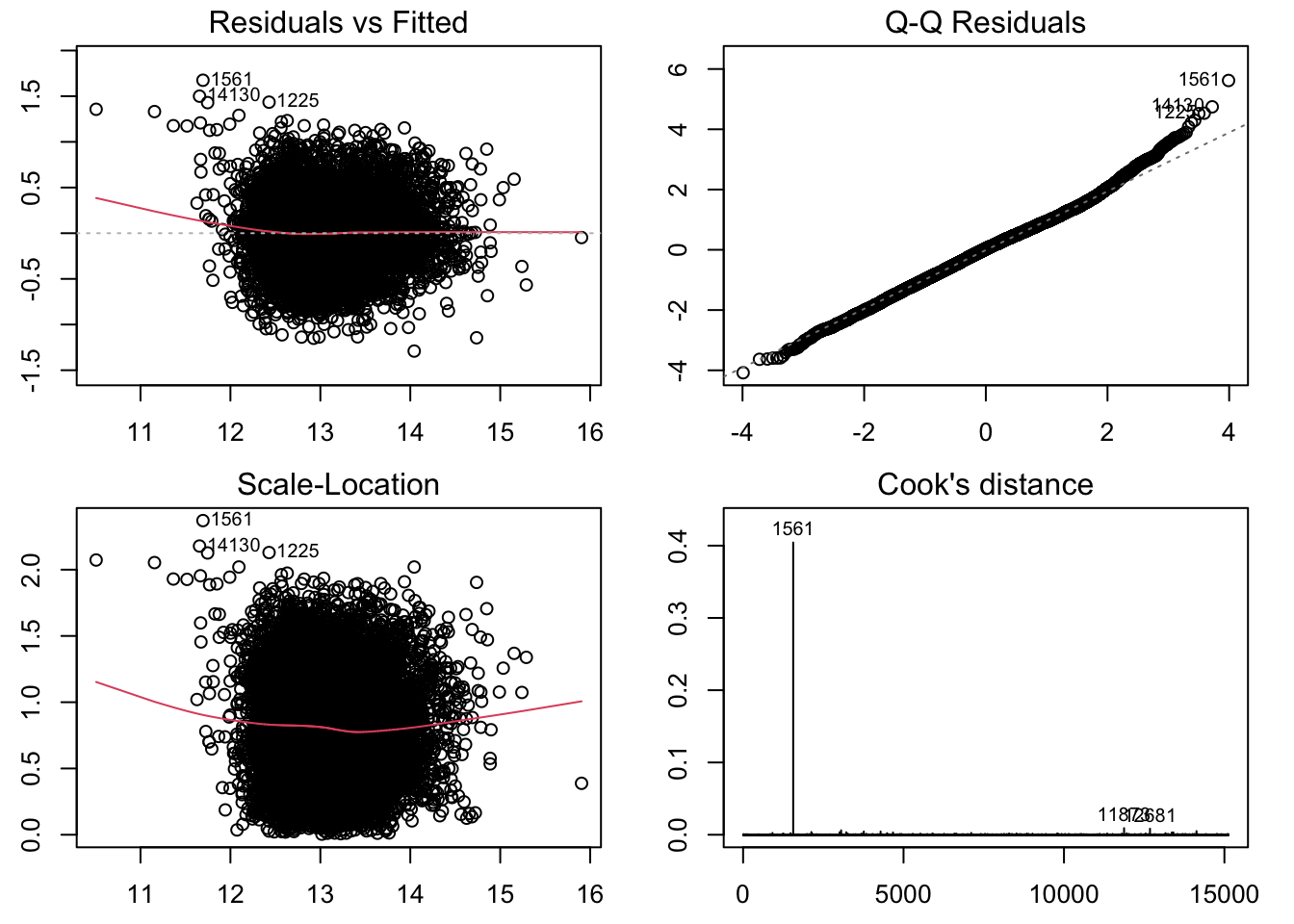
模型诊断
将绘图窗口分为 2*2 的矩阵。指定绘图区域离下边界、左边界、上边界和右边界的距离(单位为文本行数),方便画下所有诊断图。
画模型诊断图。
par (mfrow= c (2 , 2 ))par (mar= c (2.5 , 2.5 , 1.5 , 1.5 ))library (ggplot2)plot (fit.lm, which= c (1 : 4 ))
Model Optimization
从 Cook 距离图中可以看出,序号为”15871”的观测是异常点。
去除序号为”15871”的观测,重新拟合线性模型
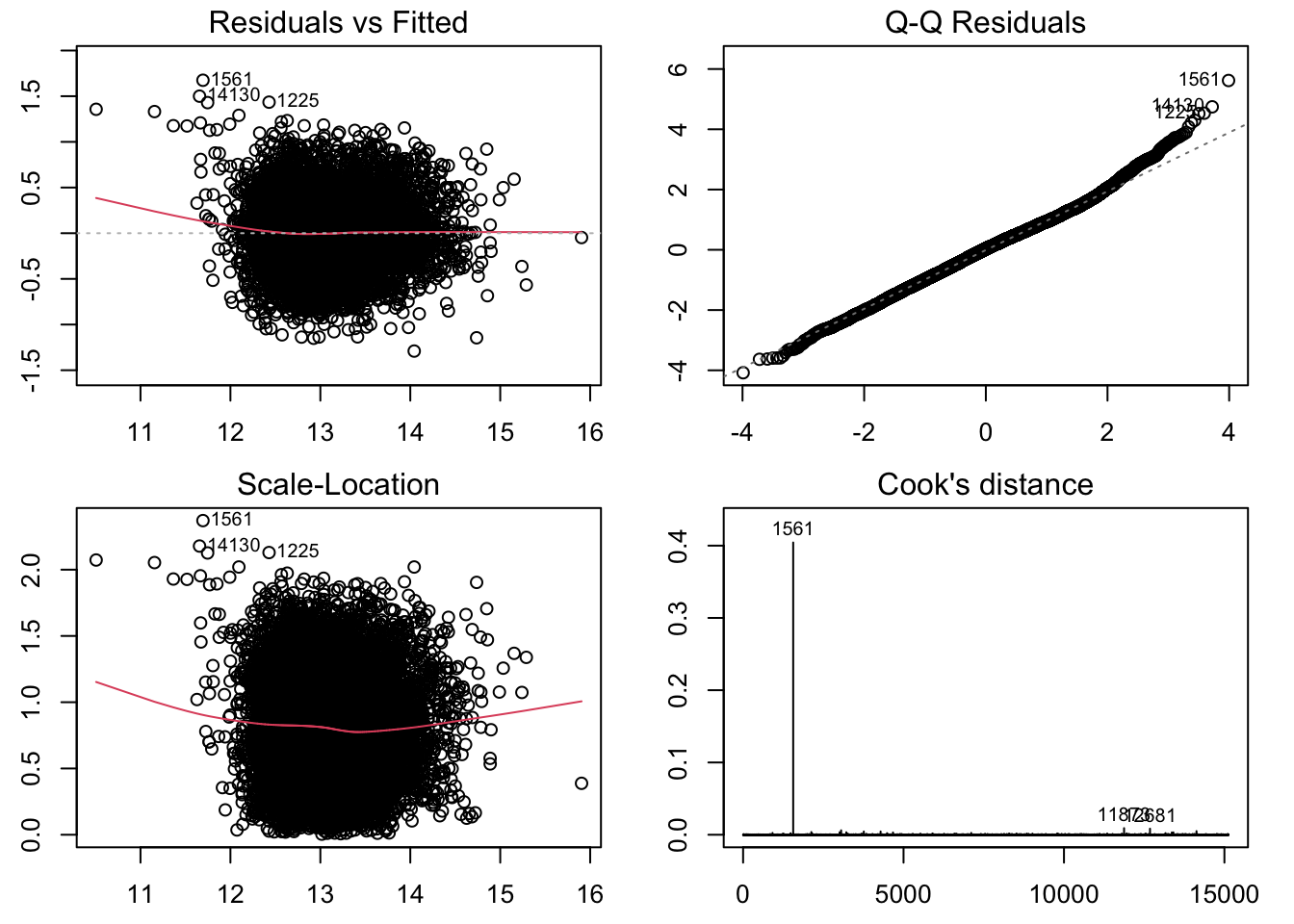
<- lm (log_price ~ log_sqft_living + log_sqft_lot + log_sqft_above + age + bedrooms + bathrooms + floors + condition + grade,data = house_learning[rownames (house_learning)!= "15871" ,])par (mfrow= c (2 , 2 ))par (mar= c (2.5 , 2.5 , 1.5 , 1.5 ))plot (fit2.lm, which= c (1 : 4 ))
使用所得的线性模型对测试数据集进行预测。
<- predict (fit2.lm, house_testing)
predition.lm 中含有预测的对数价格,exp(pred.lm) 将对数价格转换为预测的价格。将预测价格与真实价格取差值,平方之后平均,再开根号。计算出测试数据集的房屋价格预测的均方根误差。
<- sqrt (mean ((exp (prediction.lm) - house_testing$ price)^ 2 ))str (rmse.lm)
tidymodels 方法
tidymodels 方法重现了上面的建模过程,只是逻辑性和扩展性更好。
── Attaching packages ────────────────────────────────────── tidymodels 1.1.1 ──
✔ broom 1.0.5 ✔ rsample 1.2.0
✔ dials 1.2.0 ✔ tibble 3.2.1
✔ infer 1.0.5 ✔ tidyr 1.3.0
✔ modeldata 1.2.0 ✔ tune 1.1.2
✔ parsnip 1.1.1 ✔ workflows 1.1.3
✔ purrr 1.0.2 ✔ workflowsets 1.0.1
✔ recipes 1.0.9 ✔ yardstick 1.2.0
── Conflicts ───────────────────────────────────────── tidymodels_conflicts() ──
✖ purrr::discard() masks scales::discard()
✖ dplyr::filter() masks stats::filter()
✖ dplyr::lag() masks stats::lag()
✖ recipes::step() masks stats::step()
• Learn how to get started at https://www.tidymodels.org/start/
# 划分数据集 set.seed (20240206 )house_split = initial_split (house_raw, strata = price))
<Training/Testing/Total>
<16209/5404/21613>
# 训练集和测试集 house_train = training (house_split))
# A tibble: 16,209 × 10
price bedrooms bathrooms sqft_living sqft_lot floors condition grade
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 180000 2 1 770 10000 1 3 6
2 291850 3 1.5 1060 9711 1 3 7
3 229500 3 1 1780 7470 1 3 7
4 310000 3 1 1430 19901 1.5 4 7
5 230000 3 1 1250 9774 1 4 7
6 233000 3 2 1710 4697 1.5 5 6
7 280000 2 1.5 1190 1265 3 3 7
8 240000 4 1 1220 8075 1 2 7
9 309000 3 1 1280 9656 1 4 6
10 210490 3 1 990 8528 1 3 6
# ℹ 16,199 more rows
# ℹ 2 more variables: sqft_above <dbl>, yr_built <dbl>
house_test = testing (house_split))
# A tibble: 5,404 × 10
price bedrooms bathrooms sqft_living sqft_lot floors condition grade
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 221900 3 1 1180 5650 1 3 7
2 510000 3 2 1680 8080 1 3 8
3 257500 3 2.25 1715 6819 2 3 7
4 468000 2 1 1160 6000 1 4 7
5 400000 3 1.75 1370 9680 1 4 7
6 189000 2 1 1200 9850 1 4 7
7 285000 5 2.5 2270 6300 2 3 8
8 252700 2 1.5 1070 9643 1 3 7
9 329000 3 2.25 2450 6500 2 4 8
10 719000 4 2.5 2570 7173 2 3 8
# ℹ 5,394 more rows
# ℹ 2 more variables: sqft_above <dbl>, yr_built <dbl>
# 创建 recipe = recipe (price ~ ., data = house_train) |> step_log (price, starts_with ("sqft_" )) |> step_mutate (age = 2015 - yr_built) |> step_rm (yr_built)summary (house_rec)
# A tibble: 10 × 4
variable type role source
<chr> <list> <chr> <chr>
1 bedrooms <chr [2]> predictor original
2 bathrooms <chr [2]> predictor original
3 sqft_living <chr [2]> predictor original
4 sqft_lot <chr [2]> predictor original
5 floors <chr [2]> predictor original
6 condition <chr [2]> predictor original
7 grade <chr [2]> predictor original
8 sqft_above <chr [2]> predictor original
9 yr_built <chr [2]> predictor original
10 price <chr [2]> outcome original
# 定义训练参数 = metric_set (mae, rsq)# 初始化 workflow = workflow () |> add_recipe (house_rec) |> add_model (linear_reg ())# 交叉验证集 house_rs = vfold_cv (house_train, strata = price))
# 10-fold cross-validation using stratification
# A tibble: 10 × 2
splits id
<list> <chr>
1 <split [14586/1623]> Fold01
2 <split [14586/1623]> Fold02
3 <split [14587/1622]> Fold03
4 <split [14588/1621]> Fold04
5 <split [14588/1621]> Fold05
6 <split [14589/1620]> Fold06
7 <split [14589/1620]> Fold07
8 <split [14589/1620]> Fold08
9 <split [14589/1620]> Fold09
10 <split [14590/1619]> Fold10
# 拟合并评估模型 <- control_resamples (save_pred = TRUE )<- %>% fit_resamples (house_rs, control = ctrl, metrics = reg_metrics)# 在测试集上预测并收集结果 <- house_wflow %>% last_fit (house_split) %>% collect_predictions (new_data = house_test)# 输出模型指标 <- house_test_preds %>% metrics (truth = price, estimate = .pred)
# A tibble: 3 × 3
.metric .estimator .estimate
<chr> <chr> <dbl>
1 rmse standard 0.316
2 rsq standard 0.631
3 mae standard 0.250
上述代码主要完成了以下几个步骤:
使用 initial_split() 函数将数据集划分为训练集和测试集。strata = price 参数表示在划分数据时,会根据 price 列的值进行分层抽样,以确保训练集和测试集中的 price 分布相似。
创建了一个预处理 recipe,其中包括对 price 和所有以 “sqft_” 开头的列进行对数转换,以及计算房龄(2015年减去建造年份)。
定义了回归任务的评价指标:平均绝对误差(MAE)和决定系数(R²)。
初始化了一个工作流,其中包含上述的预处理 recipe 以及线性回归模型。
对训练数据进行分层交叉验证,创建了一系列的训练/验证集。
最后一步是利用交叉验证的结果来拟合工作流,并评估模型性能。
last_fit() 将工作流拟合到完整的训练数据上,然后用拟合好的模型在测试集上做预测。最后,计算了测试集上的 MAE 和 R² 指标并打印出来。
最后,数据可视化是数据科学工作中的重要一环。我们可以通过可视化来更好地理解模型的性能以及数据的特点。以下是两个常见的可视化任务:
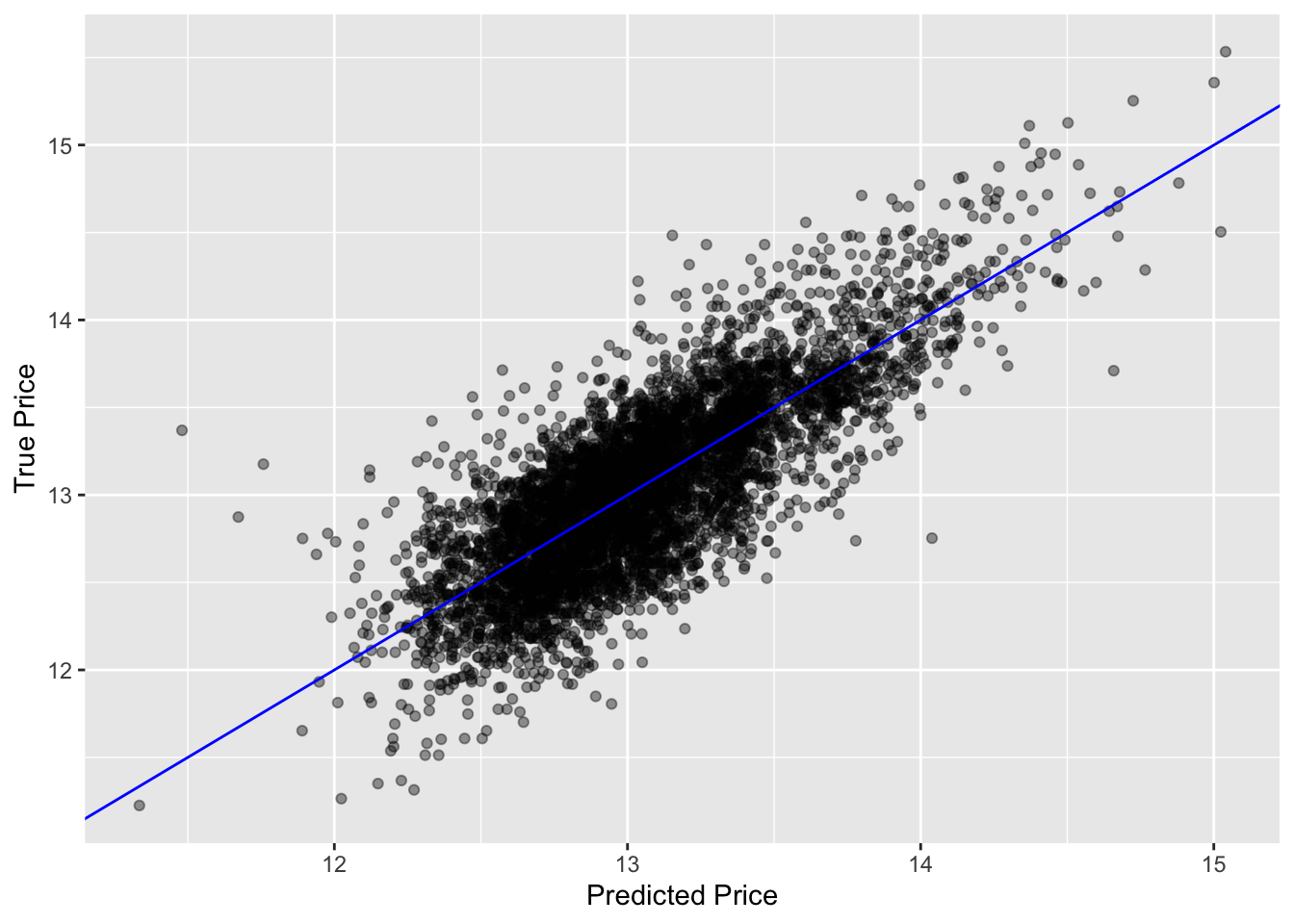
观察预测值与真实值的关系 :我们可以绘制一个散点图,横坐标为预测值,纵坐标为真实值。
ggplot (house_test_preds, aes (x = .pred, y = price)) + geom_point (alpha = 0.4 ) + geom_abline (color = "blue" ) + xlab ("Predicted Price" ) + ylab ("True Price" )
在这个图中,蓝色的线表示预测值和真实值完全相等的情况。如果模型的预测效果良好,那么点应该紧密地围绕在这条线周围。
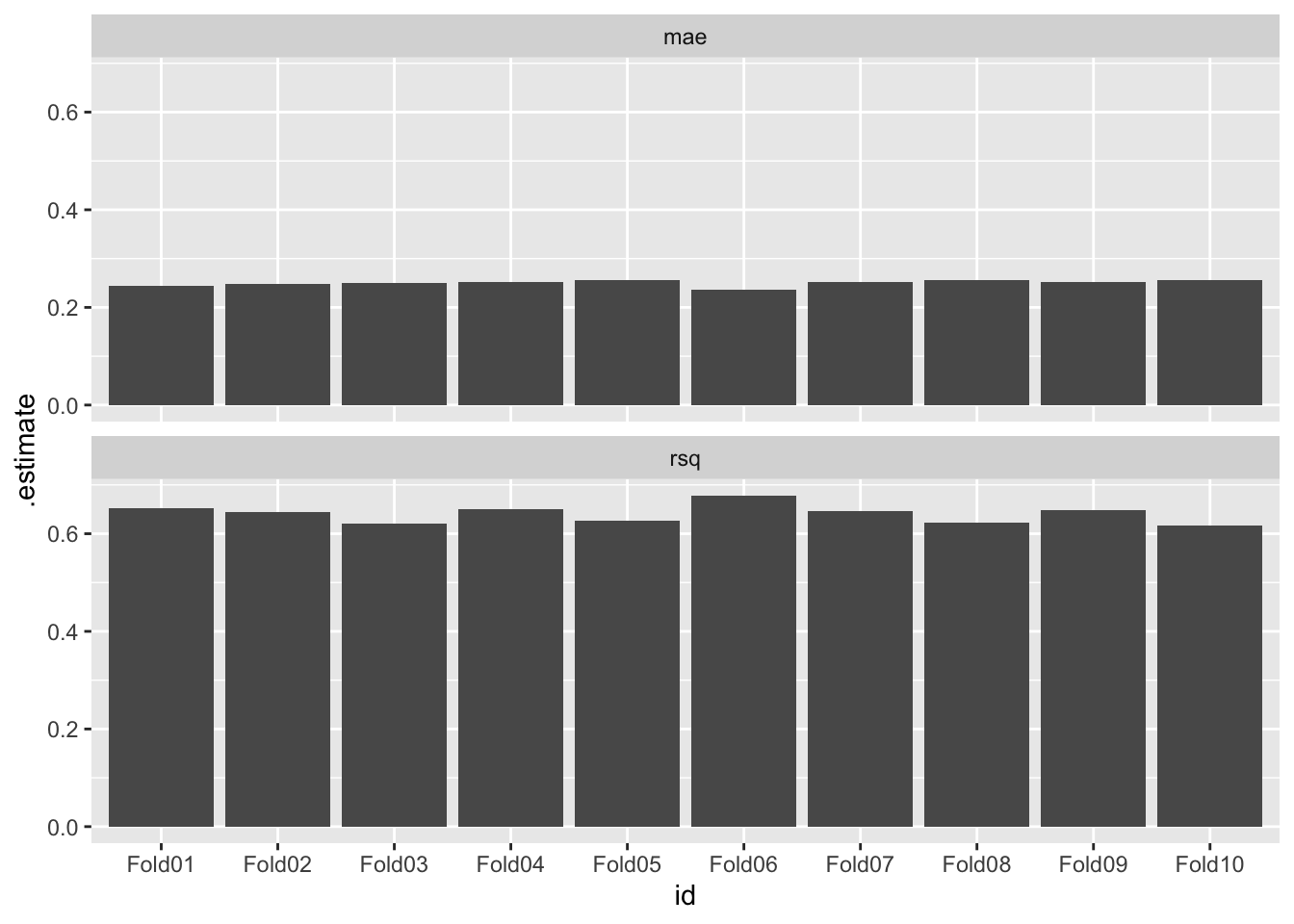
查看每次交叉验证的结果 :我们可以绘制一个箱型图,展示每次交叉验证结果的分布。
|> select (id, .metrics) |> unnest (.metrics) %>% ggplot (aes (x = id, y = .estimate)) + geom_col () + facet_wrap (~ .metric, ncol = 1 )
在这个图中,每个箱型图代表一次交叉验证的结果(即模型在不同训练/验证集上的表现)。通过查看箱型图,我们可以了解模型性能的稳定性和可靠性。
以上只是一些基本的可视化示例,具体可视化的内容和方式会依据你对数据和任务的理解进行调整。
最佳拟合结果
在 tidymodels 中,如果你使用了调参(tune)功能寻找最佳的模型超参数,那么可以使用以下方法来获取最佳的拟合结果:
# 获取最佳参数组合 <- house_res %>% select_best (metric = "mae" )# 使用最佳参数重新拟合模型 <- house_wflow %>% finalize_workflow (best_params) %>% last_fit (house_split)# 提取拟合结果 <- best_fit %>% extract_fit_parsnip ()# 拟合得到的参数 %>% tidy ()
# A tibble: 10 × 5
term estimate std.error statistic p.value
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 (Intercept) 7.78 0.0717 108. 0
2 bedrooms -0.0510 0.00370 -13.8 6.19e- 43
3 bathrooms 0.0839 0.00576 14.6 1.01e- 47
4 sqft_living 0.495 0.0157 31.5 1.25e-211
5 sqft_lot -0.0332 0.00341 -9.74 2.27e- 22
6 floors 0.0633 0.00703 9.00 2.51e- 19
7 condition 0.0364 0.00419 8.70 3.53e- 18
8 grade 0.243 0.00353 68.9 0
9 sqft_above -0.0699 0.0147 -4.77 1.90e- 6
10 age 0.00609 0.000111 55.0 0
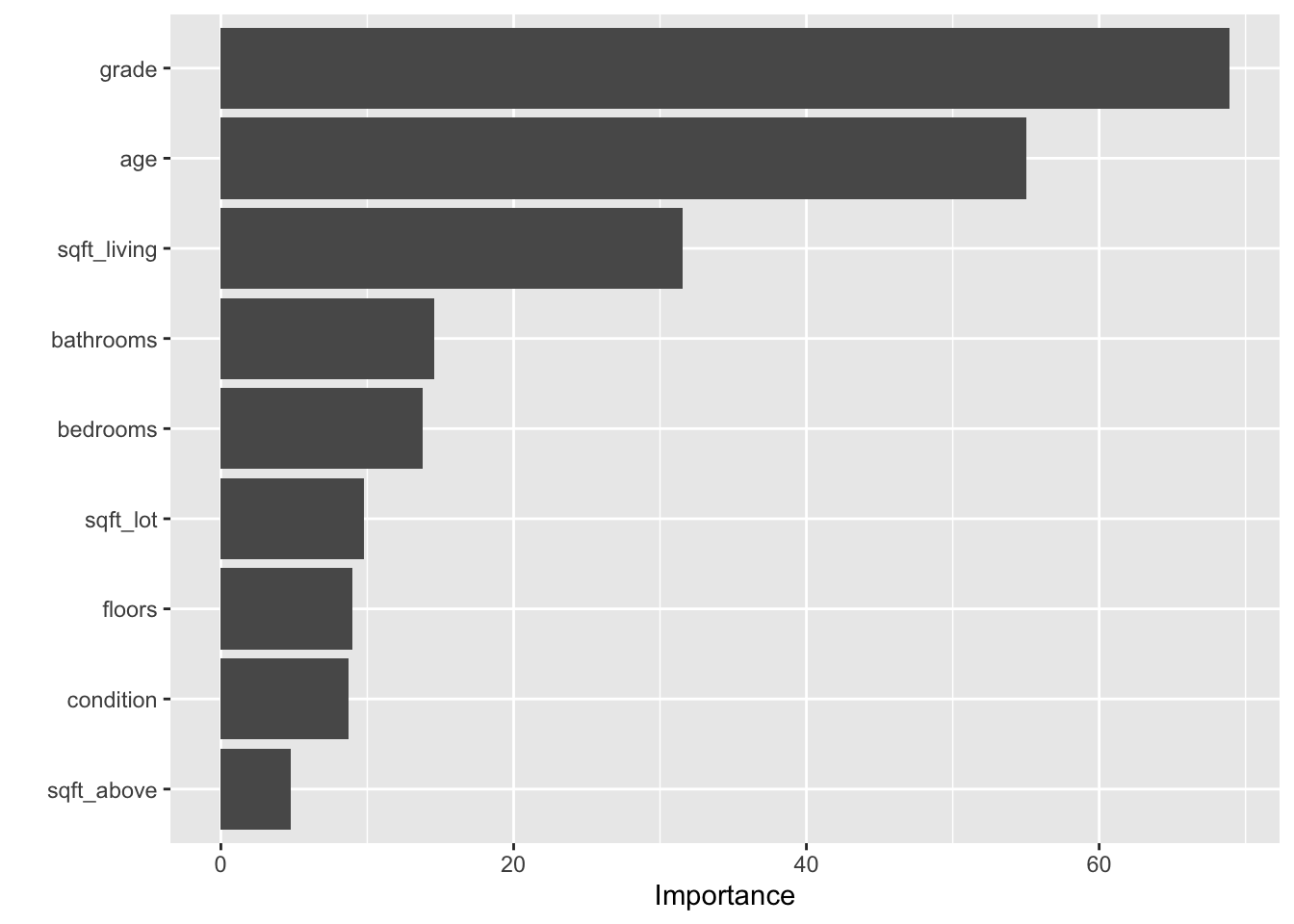
# 自变量的重要性 |> vip:: vip ()
在上面的代码中: - house_res 是你在调参过程中得到的结果,包含了所有尝试过的参数组合以及对应的评价指标。 - select_best() 函数用于选择使指定指标达到最优的参数组合。在这个例子中,我们选择使 RMSE 最小的参数组合。 - finalize_workflow() 函数将最佳参数设置到工作流中。 - last_fit() 函数则使用这个参数再次拟合模型。
然后,我们像之前一样使用 extract_fit_parsnip() 和 tidy() 函数来提取模型拟合结果。此时,fit_result 就是一个包含了最佳模型参数的数据框。