Comprehensive customization by using helper functions
The main function ggVennDiagram() accepts a list input,
and output a ggplot object. By measuring the length of input list, it
automatically applies internal functions to build a plot in two steps:
data preparation and visualization.
Data preparation was packaged into one function
process_data(). Its output is a S4
VennPlotData class object, which contains three slots,
setEdge, setLabel and region.
These slot data then can be further plotted with ggplot
functions.
See below for a better understanding.
Generate example data.
genes <- paste0("gene",1:1000)
set.seed(20231214)
gene_list <- list(A = sample(genes,100),
B = sample(genes,200),
C = sample(genes,300),
D = sample(genes,200))Then we can reproduce the plot of ggVennDiagram() with
several lines.
venn <- Venn(gene_list)
data <- process_data(venn)
ggplot() +
# 1. region count layer
geom_polygon(aes(X, Y, fill = count, group = id),
data = venn_regionedge(data)) +
# 2. set edge layer
geom_path(aes(X, Y, color = id, group = id),
data = venn_setedge(data),
show.legend = FALSE) +
# 3. set label layer
geom_text(aes(X, Y, label = name),
data = venn_setlabel(data)) +
# 4. region label layer
geom_label(aes(X, Y, label = count),
data = venn_regionlabel(data)) +
coord_equal() +
theme_void()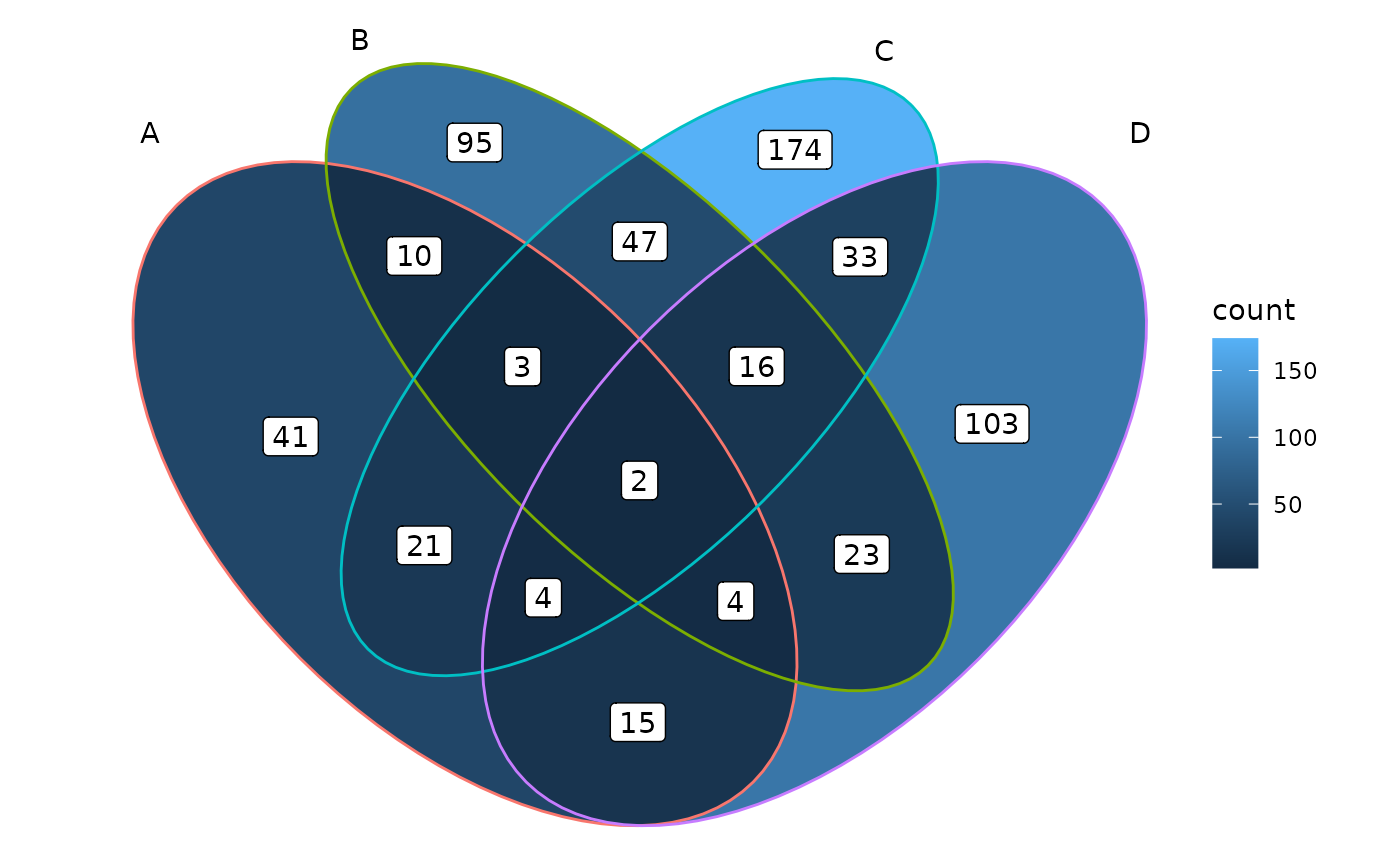
The variable data is a structured list that has three
slots.
data
#> Class VennPlotData - '401f'
#> Type: ellipse; No. sets: 4; No. regions: 15.
#> To view this shape, use `plot_shape_edge(get_shape_by_id('401f'))`.
#> To view its components, use `venn_setedge()`, `venn_setlabel()`, etc.ggVennDiagram export functions to get these data, and
they can be used for comprehensive customization in user-side.
-
Venn(): Venn object constructor, use this to construct a Venn object from list. -
process_data(): process data with a Venn object -
venn_regionedge(): get region edge data to plot -
venn_regionlabel(): get region label position to plot -
venn_setedge(): get setedge data to plot -
venn_setlabel(): get setlabel data to plot
For example, you may change edge/fill/label properties as you will.
ggplot() +
# change mapping of color filling
geom_polygon(aes(X, Y, fill = id, group = id),
data = venn_regionedge(data),
show.legend = FALSE) +
# adjust edge size and color
geom_path(aes(X, Y, color = id, group = id),
data = venn_setedge(data),
linewidth = 3,
show.legend = FALSE) +
# show set label in bold
geom_text(aes(X, Y, label = name),
fontface = "bold",
data = venn_setlabel(data)) +
# add a alternative region name
geom_label(aes(X, Y, label = id),
data = venn_regionlabel(data),
alpha = 0.5) +
coord_equal() +
theme_void()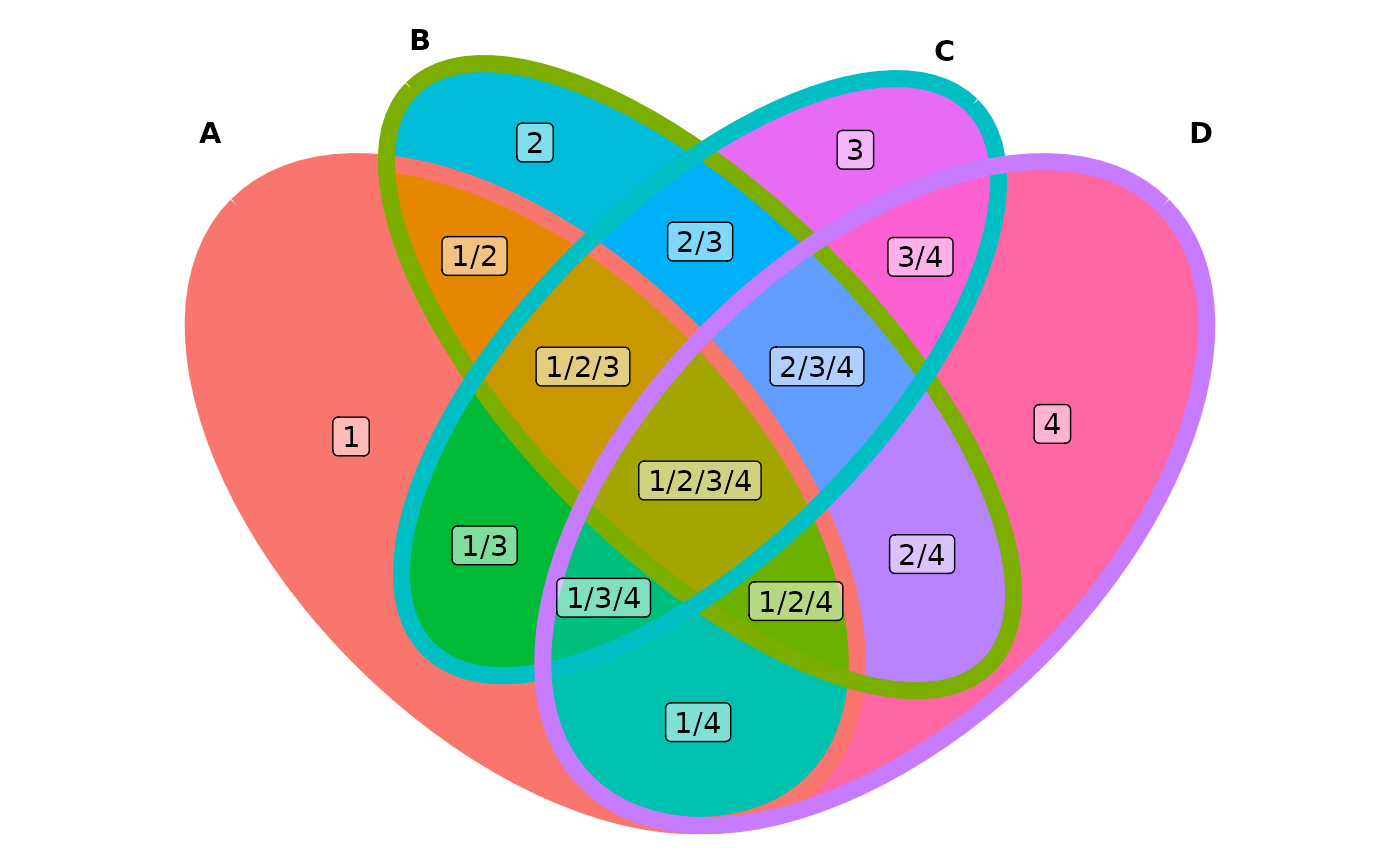
Access to classes
set.seed(20231225)
y = list(
A = sample(letters, 8) |> sort(),
B = sample(letters, 8) |> sort(),
C = sample(letters, 8) |> sort(),
D = sample(letters, 8) |> sort())
# view the list
y
#> $A
#> [1] "a" "e" "g" "o" "p" "s" "t" "v"
#>
#> $B
#> [1] "a" "d" "f" "i" "k" "s" "y" "z"
#>
#> $C
#> [1] "b" "g" "k" "o" "r" "s" "u" "w"
#>
#> $D
#> [1] "b" "c" "e" "h" "k" "q" "s" "y"Access to subset items
To view subset itmes interactively, set
show_intersect = TRUE.
ggVennDiagram(y, show_intersect = TRUE, set_color = "black")
#> Warning in geom_text(aes(label = .data$count, text = .data$item), data =
#> region_label): Ignoring unknown aesthetics: text
venn_y = Venn(y)
venn_y
#> An object of class 'Venn':
#> Slots: sets, names;
#> No. Sets: 4 SetNames: A, B, C, D.
# find the overlaping members of two or more sets
overlap(venn_y, 1:2) # members in both the first two sets
#> [1] "a" "s"
overlap(venn_y) # members in all the sets
#> [1] "s"
# find the different members between sets and set unions
discern(venn_y, 1) # members in set 1, but not in all the resting sets by default
#> [1] "p" "t" "v"
discern(venn_y, c("A","B"), 3) # members in set A & B, but not in the third set
#> [1] "a" "e" "p" "t" "v" "d" "f" "i" "y" "z"
# find the specific members in one or more sets
discern_overlap(venn_y, 1) # specific items in set 1, equals to `discern(venn_y, 1)`. Those members are not shared by all the other sets.
#> [1] "p" "t" "v"
discern_overlap(venn_y, 1:2) # specific items in set 1 and set 2
#> [1] "a"Access to plot data
venn_plot_data = process_data(venn_y)
# summary of VennPlotData object
venn_plot_data
#> Class VennPlotData - '401f'
#> Type: ellipse; No. sets: 4; No. regions: 15.
#> To view this shape, use `plot_shape_edge(get_shape_by_id('401f'))`.
#> To view its components, use `venn_setedge()`, `venn_setlabel()`, etc.Sets and labels
# get the set data
venn_set(venn_plot_data)
#> # A tibble: 4 × 4
#> id name item count
#> <chr> <chr> <named list> <int>
#> 1 1 A <chr [8]> 8
#> 2 2 B <chr [8]> 8
#> 3 3 C <chr [8]> 8
#> 4 4 D <chr [8]> 8
# get subsets, i.e., regions
venn_region(venn_plot_data)
#> # A tibble: 15 × 4
#> id name item count
#> <chr> <chr> <list> <int>
#> 1 1 A <chr [3]> 3
#> 2 2 B <chr [4]> 4
#> 3 3 C <chr [3]> 3
#> 4 4 D <chr [3]> 3
#> 5 1/2 A/B <chr [1]> 1
#> 6 1/3 A/C <chr [2]> 2
#> 7 1/4 A/D <chr [1]> 1
#> 8 2/3 B/C <chr [0]> 0
#> 9 2/4 B/D <chr [1]> 1
#> 10 3/4 C/D <chr [1]> 1
#> 11 1/2/3 A/B/C <chr [0]> 0
#> 12 1/2/4 A/B/D <chr [0]> 0
#> 13 1/3/4 A/C/D <chr [0]> 0
#> 14 2/3/4 B/C/D <chr [1]> 1
#> 15 1/2/3/4 A/B/C/D <chr [1]> 1Polygons.
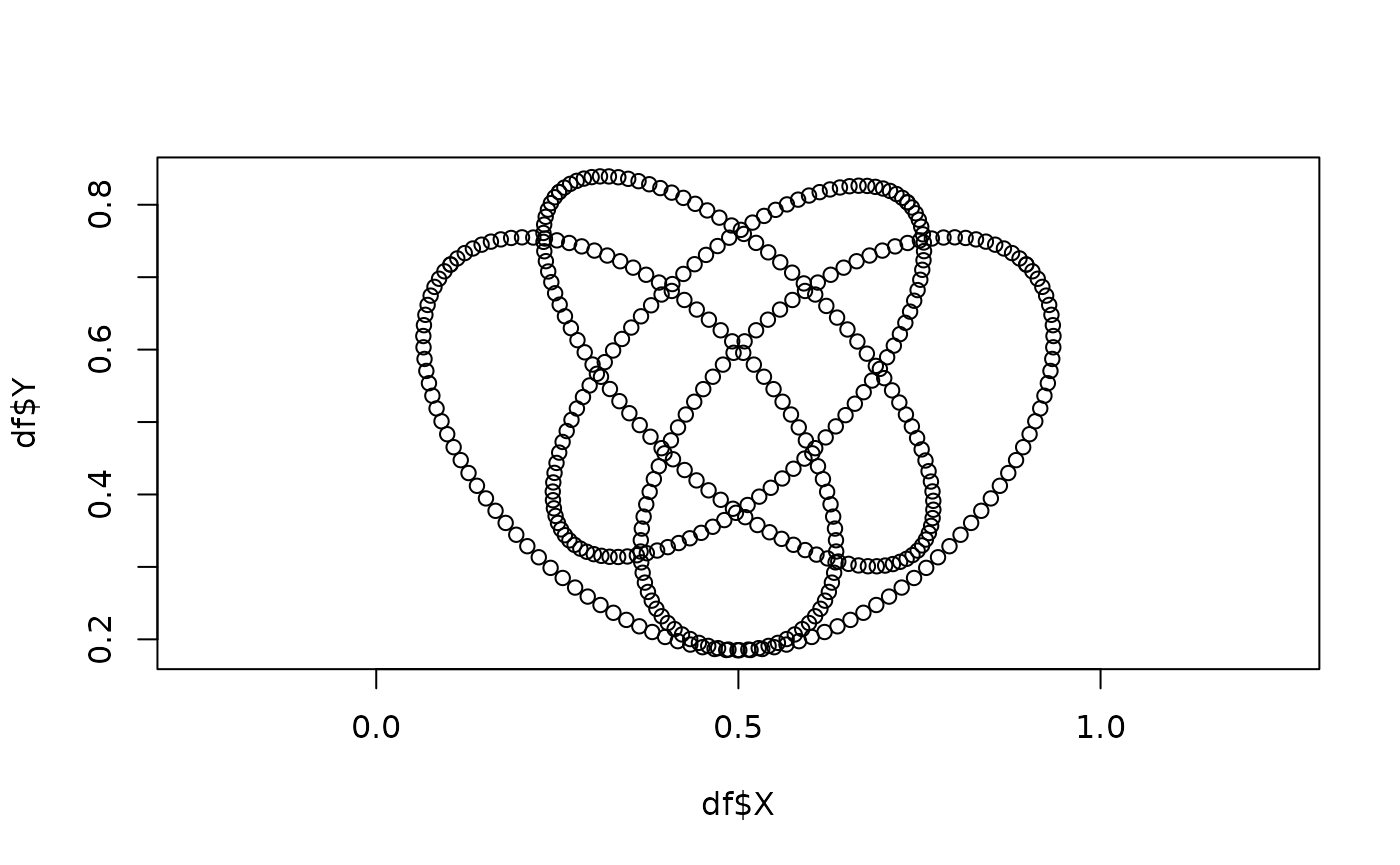
# get set edge
venn_setedge(venn_plot_data)
#> # A tibble: 404 × 3
#> id X Y
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 0.103 0.717
#> 2 1 0.0941 0.708
#> 3 1 0.0867 0.698
#> 4 1 0.0804 0.687
#> 5 1 0.0751 0.675
#> 6 1 0.0709 0.662
#> 7 1 0.0678 0.648
#> 8 1 0.0659 0.634
#> 9 1 0.0650 0.619
#> 10 1 0.0653 0.603
#> # ℹ 394 more rows
# get region edge
venn_regionedge(venn_plot_data)
#> # A tibble: 713 × 6
#> id X Y name item count
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <list> <int>
#> 1 1 0.103 0.717 A <chr [3]> 3
#> 2 1 0.112 0.726 A <chr [3]> 3
#> 3 1 0.122 0.733 A <chr [3]> 3
#> 4 1 0.133 0.740 A <chr [3]> 3
#> 5 1 0.145 0.745 A <chr [3]> 3
#> 6 1 0.158 0.749 A <chr [3]> 3
#> 7 1 0.172 0.752 A <chr [3]> 3
#> 8 1 0.186 0.754 A <chr [3]> 3
#> 9 1 0.201 0.755 A <chr [3]> 3
#> 10 1 0.217 0.755 A <chr [3]> 3
#> # ℹ 703 more rows
df = venn_setedge(venn_plot_data)
plot(df$X, df$Y, asp = 1)